Blockchains make cryptocurrency transaction data public and permanently available. They record when a transaction happened, the amounts transacted, and which addresses were involved. However, they do not contain information about the real-world services behind a transaction.
Cryptocurrency businesses and financial institutions need more context beyond just transaction amounts to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. These regulations require them to identify and report user activity that is indicative of money laundering. To do that effectively with cryptocurrency transactions, they need to know what services their customers send cryptocurrency to and receive cryptocurrency from.
As these businesses scale, they need to potentially monitor thousands of transactions across millions of customers. This is why businesses like cryptocurrency exchanges may require an automated transaction monitoring solution that constantly updates a large dataset linking transactions to real-world entities.
That’s where Chainalysis comes in. We put cryptocurrency transaction data in context for our customers by labeling addresses with the real-world entities that control them.
For example, here’s a historical transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain:
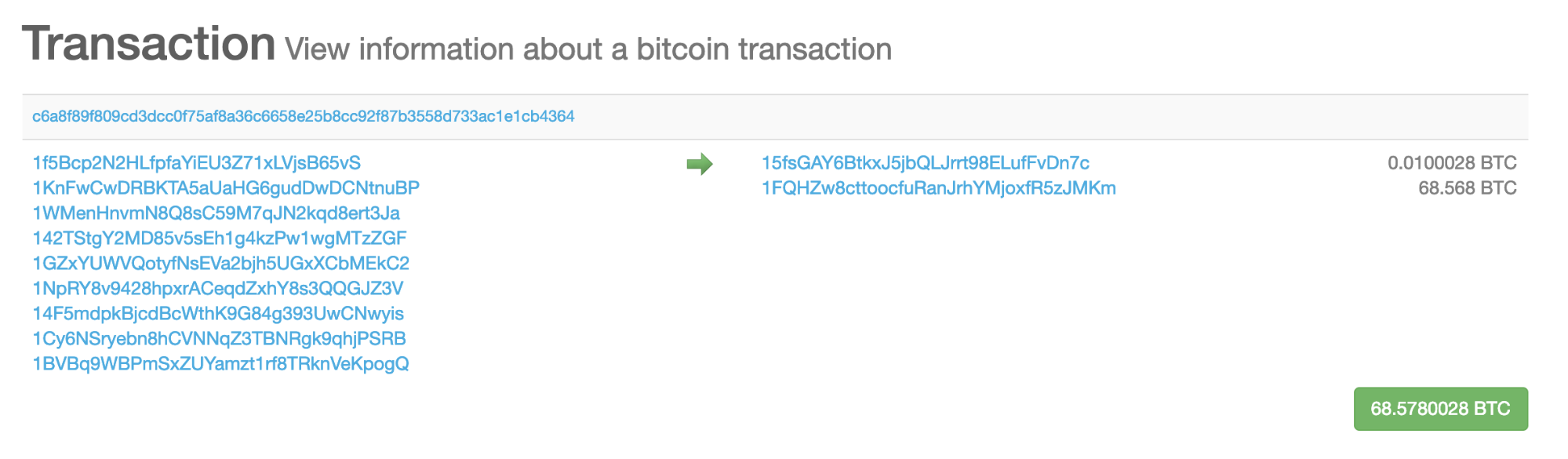
Here’s how Chainalysis labels that transaction in our software:
This helps make sense of a blockchain’s alphanumeric strings and lets exchanges know whether they are sending funds to another exchange or sending them to a darknet market.
This helps make sense of a blockchain’s alphanumeric strings and lets exchanges know whether they are sending funds to another exchange or sending them to a darknet market.
How exchanges use our KYT product
Exchanges that use Chainalysis KYT (Know Your Transaction) for AML compliance submit their transaction data, typically a list of transaction hashes, to Chainalysis to automate the process of transaction monitoring. The alternative—manually checking every possible transaction for counterparty risk—would simply be unmanageable at scale. Chainalysis’ customers may use pseudonymous identifiers when submitting their transaction data to KYT. That way, customers can help obfuscate the real-world identities of their users while still being able to map the transaction data to their own KYC database off of the Chainalysis platform.
Chainalysis KYT will flag a transaction based on indicators of risky behavior. For example, we will flag a transaction if we identify the entity behind a counterparty to be an illicit one, such as a darknet market or terrorist financing organization. Our customers can customize which entities they consider to be high and low risk. Their risk appetite and investigations are the customer’s own responsibility.
In short, Chainalysis KYT generally provides service-level identification, not individual-level identification, when attributing actions on the blockchain to a particular entity. As a result, the data that a Chainalysis customer sees in our products are not explicitly personal in nature.
We can’t speak for all other blockchain analytics vendors. It’s possible other vendors may ask for more information. But Chainalysis is primarily concerned only with service-level transaction data.
How we improve our data intelligence for our customers
When we screen a transaction in KYT for an exchange customer, we add it to our list of transactions made using that customer’s service, complementing our own independent research. These attributions collectively help all of our customers understand the various services their users may transact with and make risk determinations based on the most accurate information.
As such, our customers can establish comprehensive compliance programs and disrupt criminal networks that take advantage of cryptocurrency to traffic drugs and other illicit products, fund terrorist organizations, hack businesses, scam consumers, and more.
Ultimately, compliance and investigations solutions like ours build trust in cryptocurrency as a safe way to move value across the world.
