Blockchain technology has introduced a new era of financial transparency. In a cryptocurrency ecosystem where transactions and wallet balances are permanently recorded and publicly visible, participants are able to interact with increased trust and without the need for intermediaries. These features boost network security and can also facilitate investigations of stolen funds, transaction analysis, and identity discovery.
However, not all blockchains are transparent. Privacy coins are the major exception.
What are privacy coins?
Privacy coins are cryptocurrencies with privacy-enhancing features designed to boost anonymity and reduce traceability. They operate similarly to physical cash, but within a digital ecosystem.
When you withdraw cash from an ATM, the bank maintains a record, but has no way of knowing what you do with the money after this transaction, except if you deposit money back into an ATM. Most cryptocurrency exchanges that support privacy coins require initial identity verification of users. However, it is difficult for these exchanges to track or reveal information about subsequent transactions due to privacy coins’ inherent private features.
Although privacy coins are more resistant to tracking than other cryptocurrencies, nothing is completely anonymous. Thus, investigators with advanced tracing capabilities can follow the movement of privacy coins.
How do privacy coins work?
Privacy coins employ different methods to conceal the identities and transaction histories of their users. Here are some of the most common strategies:
- Stealth addresses enable the creation of a new address every time a user receives a cryptocurrency. Monero utilizes this method by generating a public address, a private view key to display incoming transactions, and a private spend key for sending funds.
- Ring signatures join together multiple users in a “ring” to hide their individual identities, making it more difficult to determine which user generated a given signature. This is how Monero and Bytecoin obscure transactions.
- Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge (zk-SNARKs) involves using cryptography to prove that a transaction is valid without revealing the details of the transaction. Zcash was the first privacy coin to apply zk-SNARKs on a large scale.
What are the most well-known privacy coins?
As of April 2023, the top three privacy coins by market capitalization are Monero (XMR), Zcash (ZEC), and Dash (DASH) — each with varying degrees of privacy. Through the use of stealth addresses, ring signatures, and ringCT, Monero is currently the “only major cryptocurrency where every user is anonymous by default.” Dash launched as a code fork of Bitcoin and now utilizes an encoded PrivateSend feature similar to CoinJoin. Zcash is selectively transparent, allowing users to choose when to share transaction or address information. Other popular cryptocurrencies, such as Litecoin (LTC), have implemented privacy-focused upgrades that mirror privacy coin techniques.
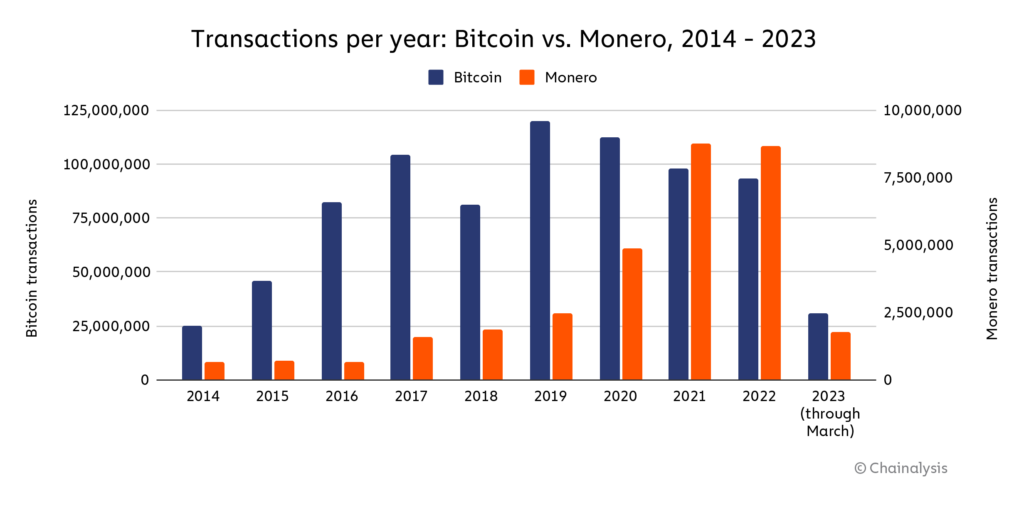
The below chart compares XMR transactions — the most popular privacy coin — to Bitcoin (BTC) transactions. The total number of BTC transactions since 2014 is approximately 790 million whereas XMR transactions total around 32 million. Regardless, XMR has grown in usage since 2014, peaking in 2021 at approximately 8.8 million transactions.
The below chart lists popular privacy coins.
Top 15 privacy coins by market capitalization
| Name | Token | Market capitalization (approx. as of 4/18/23) |
| Monero | XMR | $2.9 billion |
| Zcash | ZEC | $700 million |
| Dash | DASH | $670 million |
| Oasis Network | ROSE | $460 million |
| Decred | DCR | $320 million |
| MobileCoin | MOB | $270 million |
| Beldex | BDX | $230 million |
| Horizen | ZEN | $150 million |
| iExec RLC | RLC | $150 million |
| Keep Network | KEEP | $150 million |
| Secret | SCRT | $120 million |
| Status | SNT | $110 million |
| Dero | DERO | $110 million |
| NYM | NYM | $95 million |
| Phala Network | PHA | $90 million |
Privacy coin use cases
The anonymity of privacy coins has led many to believe they are primarily used for money laundering, hacking, and terrorist financing. Although malicious activities certainly occur on the blockchain, we have observed that most criminals still use Bitcoin because it is cross-border, instantaneous, and liquid. Privacy coins are typically not as liquid as Bitcoin, making it more difficult for criminals to acquire them and cash out into fiat currency.
Many argue that privacy coins serve important purposes. For example, a 2020 report by U.S. law firm Perkins Coie found that privacy coins do not pose more of an inherent risk to anti-money laundering obligations than other cryptocurrencies. The paper further detailed that the benefits of privacy coins are much greater than their financial risks.
Some of the legitimate use cases for privacy coins include:
- reducing authoritarian financial control. This would be especially beneficial in countries such as China, Russia, and North Korea where governments may use CBDCs and other blockchain-based applications to monitor financial activity and exclude individuals or businesses from the economy.
- protecting sensitive information. Individuals may want to obscure their wallet wealths and purchases to avoid scrutiny. For example, wealthy cryptocurrency holders have additional incentives, such as making donations off the grid and reducing exposure to hackers seeking large exploits.
Privacy coin bans
Privacy coins are legal in the United States, but other major world economies have imposed restrictions in an effort to curb money laundering and reduce organized crime. Japan banned privacy coins in 2018; South Korea and Australia followed suit, delisting Monero, Dash, Zcash, and other coins from exchanges. Dubai is the latest country to join this list in 2023, with other jurisdictions such as the European Union considering bans. A leaked draft of a proposed money laundering bill written by the EU stated that “Credit institutions, financial institutions and crypto-asset service providers shall be prohibited from keeping. . . anonymity-enhancing coins.”
Several mainstream exchanges have also stopped offering privacy coins. Bittrex, an exchange built by security engineers, announced in January 2021 that it would soon remove popular privacy coins and encouraged users to withdraw their tokens before the deadline. Similarly, Kraken delisted Monero for its UK customers, BitBay ended Monero support, and Huobi removed seven privacy tokens due to “new financial regulations.” Such developments have led many observers to wonder whether privacy coins will survive in the long-term.
The future of privacy coins
As the cryptocurrency ecosystem advances, we will continue to see tokens with diverse use cases and characteristics. Thus far, privacy coins have challenged traditional blockchains by providing means of transacting with greater anonymity and flexibility, but have also raised questions about transparency and trust.
To maintain a safe cryptocurrency ecosystem, neither full transparency nor total anonymity is ideal. Regulators require appropriate levels of legal authority and oversight to reduce malicious activities and protect participants – whether with privacy coins or other cryptocurrencies. At the same time, businesses require tools to tackle illicit activities and preserve sensitive information. Bitcoin represents a balance between the two, promoting privacy and financial freedom while offering enough transparency to prevent abuse by bad actors.
This material is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to provide legal, tax, financial, or investment advice. Recipients should consult their own advisors before making these types of decisions. Chainalysis has no responsibility or liability for any decision made or any other acts or omissions in connection with Recipient’s use of this material.
Chainalysis does not guarantee or warrant the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, suitability or validity of the information in this report and will not be responsible for any claim attributable to errors, omissions, or other inaccuracies of any part of such material.
