Since Bitcoin’s launch in 2009, cryptocurrency has driven new markets, spurred advancements in financial infrastructure, and driven innovative thinking in how to meet the world’s economic needs.
Stakeholders such as governments, industry operators, and traditional financial institutions need a shared understanding of the players in the cryptocurrency ecosystem in order to drive continued growth and adaptation. Key to identifying and safely approaching new opportunities is an understanding who are the entities conducting cryptocurrency transactions and the level of risk and illicit activity associated.
Chainalysis demystifies cryptocurrency. As the industry’s leading provider of blockchain analysis, investigations, and compliance software, we empower banks, businesses, and governments to understand which entities are transacting with cryptocurrency so that the industry can continue to grow safely and sustainably.
In this guide, we use our comprehensive, best-in-class, blockchain dataset along with decades of combined investigative experience, to break down the key players in cryptocurrency transactions according to the level of risk they present.
How we categorize the key players in cryptocurrency
The easiest way to group the entities transacting with cryptocurrency is to think about the ways cryptocurrency is used.
- Mining
- Storage of funds
- Investing and exchanging
- Buying and selling of legal goods and services
- Obfuscating activity for privacy reasons or to conceal illegal activity
- Buying and selling of illegal goods and services
- Stealing or scamming
The entities associated with each of these use cases make up the services and organizations, described throughout this guide, which we have organized according to risk level.
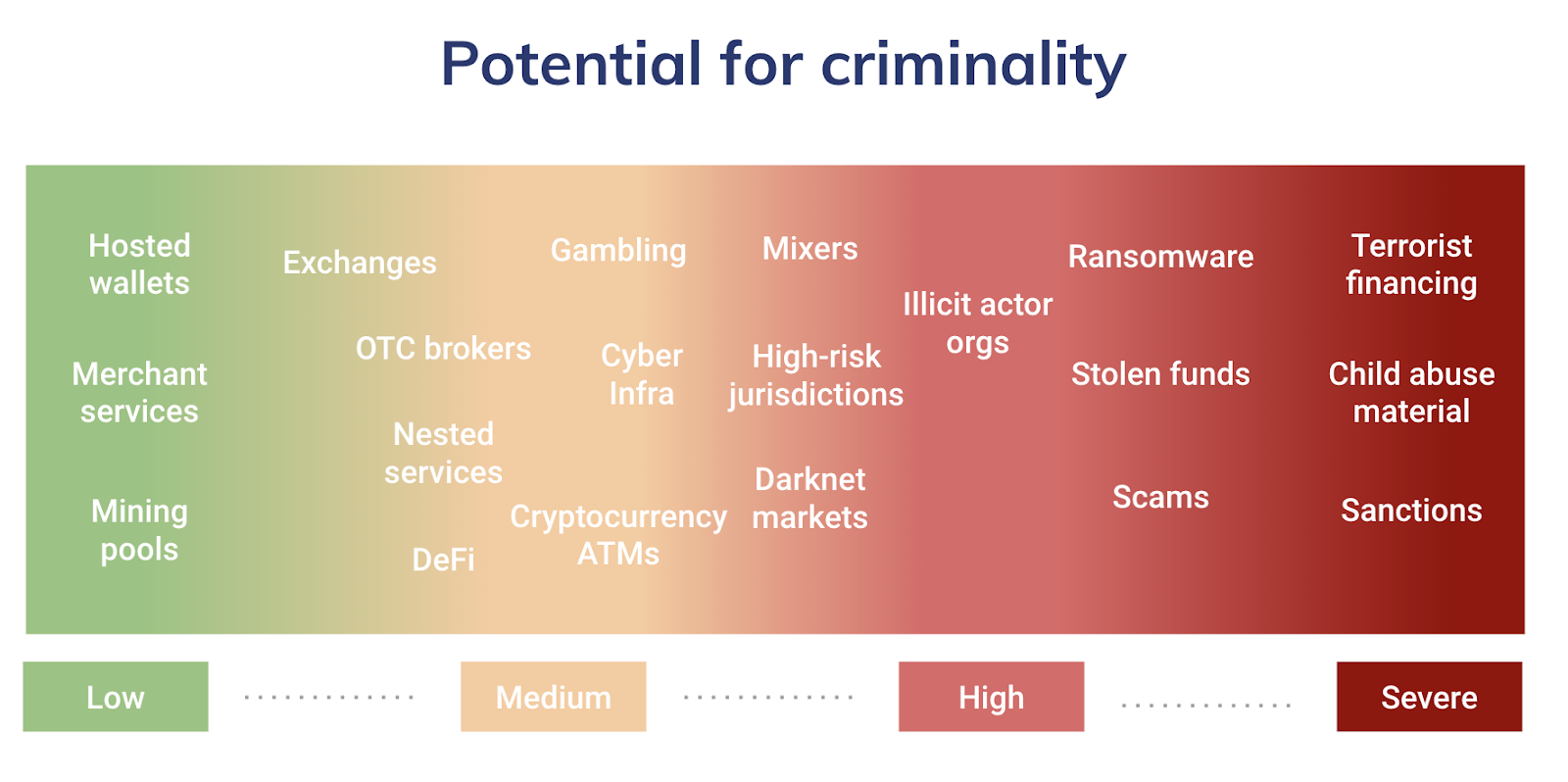
On the left are services such as hosted wallets and merchant services, which are used less often for illicit activity and are therefore lower risk.
On the right are entities such as terrorist financing schemes, which are illegal under any circumstances and therefore rated as severely risky.
Those in the middle aren’t universally considered illegal, but are often linked to or used to aid in criminal activity. For example, while gambling is perfectly legal in many jurisdictions, it has also historically been used as a means of money laundering.
These risk levels only represent the services themselves, and are not enough on their own to assess the risk level of a specific entity. The only way to do that is to analyze that entity’s cryptocurrency transactions and counterparties in greater detail.
If you’re new to the cryptocurrency ecosystem, this guide will provide you with an understanding of how different groups use cryptocurrency and what you should be on the lookout for to limit risk of exposure to illicit activity.
Let’s dive in, starting with merchant services.

Merchant services providers allow mainstream businesses to accept cryptocurrency as payment for everyday customer purchases, whether they’re happening online or in person. Think of them as regular payment processors, like Stripe or Square, except compatible with cryptocurrencies. Merchant services allow people to use cryptocurrency the same way they use fiat currency.
Why would somebody — consumer or business — want to use cryptocurrency over fiat currency? There are lots of reasons, but the biggest is the reduction of fees. Conventional payment methods like credit cards carry a fee for each transaction, which means the business has to either absorb the cost or pass it on to the customers.
Cryptocurrency payments are more direct transactions, which means they can be processed more cheaply than credit card payments. The same goes for cross-border payments and remittances.
As cryptocurrency adoption grows, merchant services adoption is also growing, with global companies like Starbucks, Whole Foods, Tesla and others now accepting cryptocurrency payments. In aggregate, merchant services usage has trended upwards since 2020 after a nearly two-year lull, with some dramatic spikes and declines during and after the Bitcoin price boom in 2017.
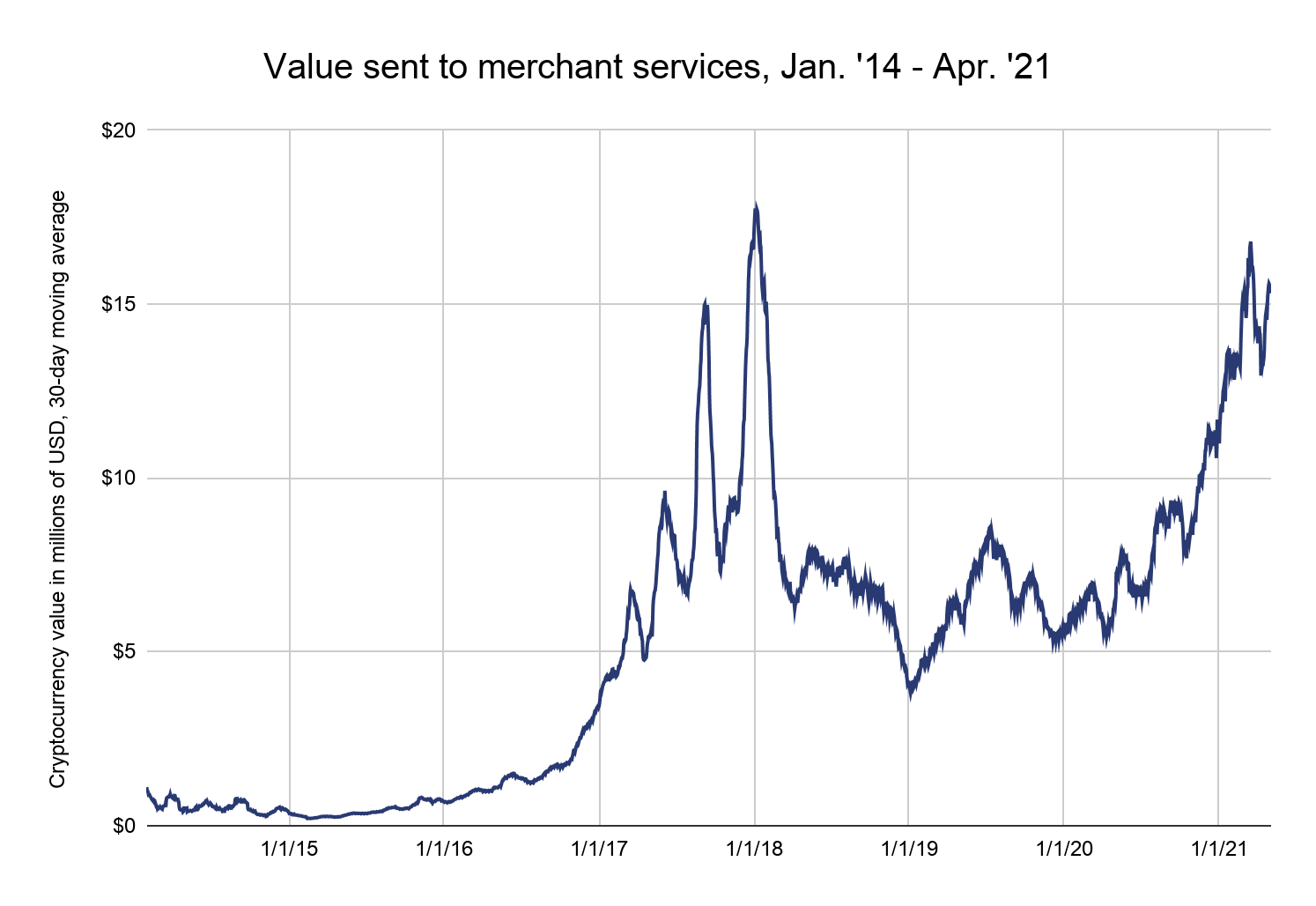
The merchant services category is generally a low-risk category. Users are typically traditional businesses and their customers. However, it’s worth noting that scammers sometimes integrate merchant services with malicious websites to accept cryptocurrency payments from their victims.
Download the full report here to get the full rundown on 19 more cryptocurrency service and organization categories you need to know about!
