While the concept of the blockchain was introduced over a decade ago, it took some time for blockchain gaming to make its debut. After years of speculation on how blockchains could augment video games with player rewards and ownership of digital content, Axie Infinity burst onto the scene in 2020 and became the biggest web3 game to date. While Axie Infinity suffered a $600 million hack to its cross-chain bridge protocol in March 2022 and has seen serious declines in usage since, many remain excited about how blockchains, video games, and metaverses can intersect to create new economic paradigms in the world’s biggest entertainment industry that benefit both players and companies.
Why is there so much excitement around blockchain gaming? Participants value this ecosystem as it affords more control over the experience, letting them earn tokens or in-game assets, and sell them on decentralized marketplaces. As of now, interest in blockchain gaming shows no signs of stopping — according to a report by Allied Market Research, the 2022 market was valued at $4.83 billion, and it’s estimated to grow 68% by 2030.
In this blog, we’ll cover:
- What are blockchain games?
- How blockchain technology and gaming relate
- How blockchain can improve gaming
- Limitations and challenges of blockchain games
- Examples of blockchain gaming projects
- Blockchain gaming for developers
- The future of blockchain games
What are blockchain games?
Blockchain games, simply put, are video games that are administered with or built in part using blockchain technology. Depending on the exact way they leverage blockchain technology, they’re sometimes referred to as crypto games, NFT games, web3 games, or metaverse games. The technology underlying blockchain games mean they can differ from traditional video games in several important ways:
- Decentralization: Blockchain games can be built and maintained by many independent members of a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) rather than by a corporation or single entity, making it harder to compromise or discontinue them. Of course, traditional video game makers could still offer blockchain games with similar benefits without managing them via a DAO.
- Interoperability: Blockchain-based games can interact seamlessly with other blockchain games, expanding the potential market for assets associated with any given game.
- In-game ownership and play-to-earn incentives: Blockchain games present opportunities for users to buy or win digital assets like native tokens or NFTs. Gamers can keep or sell these assets on decentralized marketplaces in exchange for fiat money.
- User portability of data: Blockchain gaming can put gamers in control of their own data and assets, allowing them to move them from one platform or game to another as it suits them
How blockchain technology and gaming relate
How can blockchain technology and video games come together? The technology that underpins blockchain games includes everything from the smart contracts that facilitate in-game transactions to creation of in-game digital assets like NFTs to validating and recording all blockchain transactions that happen in game. That same technology allows players to earn monetary incentives through play. Blockchain technology is even used to fund blockchain game projects — native tokens are sold through initial game offerings (IGO) or initial coin offerings (ICO) to developers, gamers, and institutional investors interested in the games.
NFTs and gaming
In the world of blockchain gaming, NFTs (or non-fungible tokens) are unique digital assets that gamers can purchase, use in-game, and sell to other gamers and collectors. These assets are generally produced in limited supply, which promotes digital scarcity and adds to their value. Certain NFTs may be compatible or transferable to other games, so that holders can use them across blockchain gaming ecosystems, a prime example of interoperability. As is the case with all NFTs, the ownership of NFTs associated with games is secured on the blockchain so that they cannot be duplicated, and their authenticity is assured.
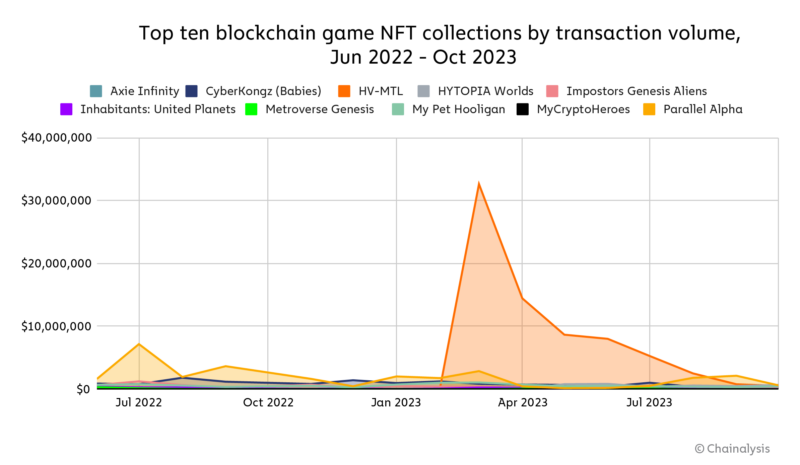
Using OpenSea rankings, the chart above shows the top ten blockchain game NFT collections by transaction volume between June 2022 and October 2023. Since the Axie Infinity hack and crypto’s market woes late last year, the NFT buying frenzy has subsided.
Metaverse games
Metaverse games are virtual worlds with cryptocurrency-based financial systems. These games provide fully immersive environments where players use characters to interact with other players in real-time, 3D experiences. Some metaverse games even harness virtual reality (VR) technology to enhance immersion and realism.
When it comes to popular metaverse games, Decentraland is a prime example. In this Ethereum-based metaverse, players use tokens in the virtual world to make personas, buy land (represented by NFTs), and even develop virtual experiences like concerts or art galleries for other players to enjoy. Players can also generate income by renting or selling their virtual land. Decentraland is governed by a DAO and in order to join or vote on issues, members must buy MANA (the game’s native token), which they can use to purchase NFTs that represent virtual lands or virtual worlds in the game.
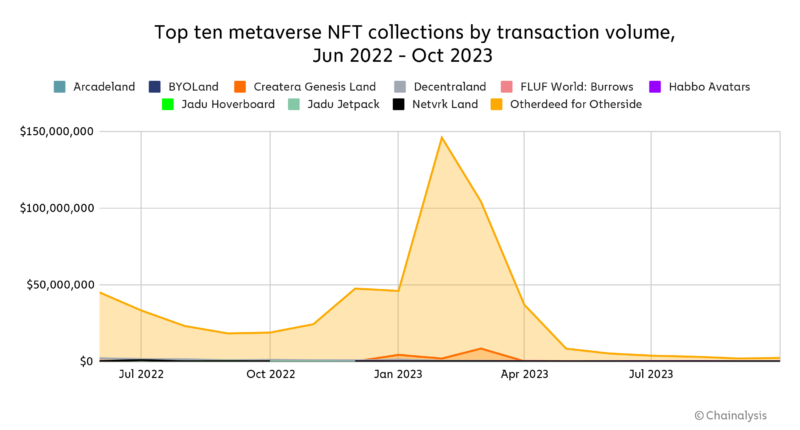
Using OpenSea rankings, the chart above shows the top ten virtual world NFT collections by transaction volume from June 2022 to October 2023, with Otherdeed for Otherside the clear leader.
Blockchain video games, while seldom linked to metaverse projects today, have many of the same ambitions:
- To build more open-ended economies
- To connect individuals and communities
- To push the boundaries of digital ownership
- To decentralize and share the value they create
- To make the virtual world as immersive as reality
They’ve also, like metaverse projects, recently exploded in popularity and funding. DappRadar recently reported that blockchain gaming activity has increased 2,000% over the last year. Furthermore, blockchain-based game companies fundraised $2.5 billion last quarter, up 150% from the quarter before.
But what about traditional games and game companies? What would happen if already-popular games adopted NFTs and cryptocurrency? Let’s take a look and see (with a healthy suspension of disbelief).
Play to earn
One major advantage of blockchain games over traditional games are play-to-earn (P2E) incentives — the ability to earn native crypto tokens or NFTs from in-game play or time spent in a blockchain game. In P2E games like Axie Infinity, players can trade these assets with other players in-game or sell them on decentralized NFT marketplaces. By providing financial incentives, P2E crypto games attract players and keep them invested in game play.
Ownership of in-game assets
In the metaverse gaming model, players can buy and sell in-game assets like NFTs. As mentioned, the ability to do so allows players more control over their gaming experience, in stark contrast to traditional games. Using decentralized networks, blockchain games secure player assets via encryption and since these games don’t live on centralized servers, it makes it more challenging for cybercriminals to hack player assets or tokens. The transparency of blockchain ledgers also helps players keep track of their assets and transactions, reinforcing a sense of ownership that’s not present in regular video games.
How blockchain can improve gaming
Blockchain gaming offers several unique benefits to both players and game publishers.
In traditional gaming, the company that developed the game controls all the data and associated servers; it is a closed ecosystem. So, if the company decides to end the game, the players have no say. Conversely, when game assets and data are stored on a blockchain, the game is more resilient. And whereas, a traditional game relies on subscription models or purchase of assets that gamers can’t take with them, the blockchain gaming model allows users to earn and own assets in perpetuity and use them in other games or virtual worlds. Because blockchain gaming gives users control over assets, it makes the experience more compelling than traditional games.
In addition to that advantage, the decentralized nature of blockchain games encourages more community participation and personal investment. Blockchain games are often governed by collectives like DAOs that solicit user feedback, so they typically have more player-driven improvements than traditional games do, and these collectives have played a formative role in shaping the blockchain gaming ecosystem.
Another advantage of crypto games is that because blockchains are transparent and immutable, players can’t cheat the system, which builds user trust. Smart contracts verify in-game activity through cryptography, ensuring that play is fair.
Limitations and challenges of blockchain gaming projects
As one of the first video games, Tennis for Two, was created in 1958, traditional video games have had several decades to mature, both in design and concept. As the newest kid on the block(chain), crypto games have some catchup to play, particularly with user experience (UX). In blockchain games, UX limitations show up in a variety of ways:
- For players without crypto knowledge, blockchain games could be frustrating because purchasing in-game assets requires making crypto transactions. Since this isn’t yet common knowledge in today’s society, it presents a barrier to entry for some people.
- Network scalability is an ongoing challenge, particularly for Ethereum, where many blockchain games reside. Network congestion can cause in-game delays when transactions are required, which can discourage users.
- When the network is congested, transaction fees will also increase, frustrating users and making games more expensive to play.
- Any blockchain network technical issue could adversely affect game play.
- From a graphics perspective, blockchain games lag behind the sophistication of traditional gaming, as do the plots and complexity of the games. We expect blockchain gaming will overcome this challenge as more innovation occurs with decentralized apps (dApps).
A blockchain gaming thought experiment: EA Sports on the blockchain
In fiscal year 2021, Electronic Arts (EA) generated $1.62 billion from its FIFA, Madden, and NHL Ultimate Team offerings.
In Ultimate Team (UT), players assemble, trade, and compete against one another with a squad of athletes, each of which are represented by a trading card. Players can buy packs of 12 to 30 of these trading cards with either points, which can be purchased with real money, or coins, which can be collected for free by playing. Players can then sell the cards they’ve drawn to other players in exchange for coins – but they can never convert game currency into points or real money.
At least in theory. In practice, despite EA’s best efforts, there’s a gray market for these coins that undercuts EAs pricing. For example, to buy an Ultimate Pack – EA’s highest-tier and most expensive pack – players must spend either 2,500 points or 125,000 coins. Bought with points purchased from EA, this pack costs $23; bought with coins purchased on the gray market, this pack costs $6.50.
Source: PlayerAuctions
In other words, this gray market both threatens EA’s main revenue stream and makes “good citizen” players worse off. When third parties sell their coins for real currency, EA gets nothing – but players get three times the value for money.
But what if, instead of maintaining a closed-loop economy and forgoing this revenue leakage, EA minted their trading cards as NFTs, which could then be sold between players on a secondary market? How would this alter their revenue – and create new ways for players to make money?
For one thing, it would introduce a new revenue stream for EA. Usually, when an item is minted as an NFT, a portion of every sale is passed back to its creator as a royalty. UT already features a 5% transaction fee on its player-to-player market – so this is hardly unprecedented– but today it’s not an actual revenue stream. Instead, it’s a “gold sink” – a way to prevent coins from hyperinflating.
For another, it would heighten the concept of rarity. While no cards in today’s UT economy have a predefined supply, this is the de facto standard for NFTs – and a key reason why they can fetch such high prices.
Lastly, it would give UT players the ability to make money. This is win-win: if players can sell their cards for cryptocurrency, they can earn back some or all or even multiples of their original spending; if EA enables these trades, they can collect a small slice of every sale price.
Modeling Ultimate Team with NFTs
We now construct a simple financial model for both EA’s revenue and Ultimate Team players’ earnings in a game mode reimagined with NFTs.
Assumptions:
- 25 million active players. Ballpark estimate based on EA statements.
- $65 annual player spend. Ultimate Team revenue ($1.62 billion) divided by active players.
- 5% resale royalties. A common rate for NFTs.
- NFT primary sale price = secondary sale price. Some cards will surely rise in value following their primary sale while others will fall, so for simplicity’s sake, our model assumes that in aggregate, all cards’ secondary sale prices will equal primary sale prices.
Variables:
- Annual resale volume. Our model projects NFT sales revenue for both EA Sports and its UT players at three different possible levels of annual NFT resale volume: 100%, 300%, and 500%. 100% resale volume would mean that for every $1 of annual player spend on primary NFT sales, there is $1 of secondary market sales. 300% would assume $3 of secondary market sales, while 500% would assume $5.
Results
| EA revenue: UT x NFTs | Annual resale volume | |||
| 100% | 300.00% | 500.00% | ||
| Annual EA Sports revenue assuming $65 per player spend on primary card sales | $1,706,250,000 | $1,868,750,000 | $2,031,250,000 | |
Interpretation: NFTs could generate significant additional revenue for EA Sports. Under our lowest resale volume model (100%), in which players spend $65 on NFTs and engage in $65 worth of secondary market activity, EA generates $1.7 billion in annual revenue – $81 million more than they do today. At 300% resale volume, EA generates $1.87 billion – $244 million in additional revenue. And at 500% resale volume, EA generates over $2 billion in annual revenue – $406 million more than today.
But how do the players fare?
| Player earnings: UT x NFTs | Annual resale volume | |||
| 100.00% | 300.00% | 500.00% | ||
| Annual player revenue assuming $65 per player spend on primary card sales | $1,543,750,000 | $1,381,250,000 | $1,218,750,000 | |
Interpretation: Introducing NFTs could create a first-of-its-kind market for players to profit. Under our lowest resale volume model, players collectively realize $1.54 billion in annual earnings – none of which they realize today. At 300% resale volume, players’ earnings fall to $1.38 billion. And at 500% resale volume, players’ earnings rest at roughly $1.22 billion. In this model, players’ total earnings fall as resale volume rises, because more resales means more fees, and our model assumes no increase in card value upon resale on average — again, some cards will rise in value, while some will fall. However, total player earnings could increase if the average card price rose over time, as is the case with many NFT collections generally.
It’s worth noting that in this model, primary sales would still be EA’s main revenue driver. But the secondary sales, while accounting for only a fraction of EA’s $1.87 billion in revenue, would benefit players immensely. Even if we relax the assumption that the NFTs hold their original value, players of Ultimate Team could still walk away with hundreds of millions in earnings collectively – a far cry from the $0 they earn as “good citizens” today.
Furthermore, because in this model players recognize that they have a chance to resell their cards for a profit, it may attract an even higher annual player spend than our original $65 assumption.
Examples of blockchain gaming projects
As mentioned at the outset, Axie Infinity is perhaps the most well-known blockchain game project. A P2E game, it’s named for axies, which are cute monsters that gamers can collect, breed, and use in battles. Players can also trade these collectibles on NFT marketplaces. Our earlier example in metaverse games, Decentraland, uses NFTs to represent virtual land and virtual worlds, collectibles that players also trade on decentralized marketplaces. This model is one that traditional video games could follow to enter the blockchain ecosystem. On that topic, in our State of Web3 Report, we conducted a blockchain game thought experiment for EA Sports. It demonstrated how this traditional game developer could break out of its closed-loop economy and mint trading cards as NFTs to generate significant additional revenue.
Blockchain gaming for developers
For new and seasoned blockchain developers alike, there’s much to consider when diving into blockchain game development and projects. The first consideration is the platform on which to build. As the network that first created NFTs in 2014, Ethereum may seem the obvious choice, but today, several other blockchains are used for NFT development, each with distinct advantages.
Beyond choosing networks, here are other considerations for blockchain game developers:
- Blockchain game creators must understand regional regulatory obligations in order to comply with laws.
- Smart contracts are the cornerstones of blockchain gaming because they’re responsible for managing transactions and in-game assets. Experience creating smart contracts is critical for blockchain game development success.
- A plan for revenue generation is key, whether through the sale of NFTs, in-game assets, or transaction fees.
- Relatedly, expertise on how to design and mint NFTs is essential to blockchain game development.
- As mentioned earlier, many blockchain games don’t place sufficient emphasis on graphical design or sophisticated and engaging game play. Metaverse games that prioritize these considerations have the opportunity to stand out.
- The world of blockchain gaming has much overlap with decentralized finance (DeFi) — DeFi protocols are often used for lending in games or for in-game transactions. Blockchain game developers with demonstrated expertise in this area will have more opportunities.
- Blockchain games should have easy-to-follow tutorials for players as well as clear documentation for developers who want to participate in the game’s development.
- Security is critical because without the proper protections in place, blockchain games are vulnerable to hacks. Once an exploit occurs, in addition to the damage wrought on players, it’s hard to regain user and developer trust or find new investors to support the project.
What does the future hold for blockchain gaming?
For blockchain gaming to evolve and grow, the ecosystem must consider some seminal questions. For instance, how could developers educate and incentivize traditional video game players to try crypto games? What kinds of policies could blockchain gaming projects enact to give people even greater control over their own gaming data? How can blockchain game developers prioritize interoperability so that players can move more effortlessly between games and crypto networks? How can DAOs govern metaverse gaming projects or evangelize blockchain gaming in a way that encourages greater adoption?
Blockchain gaming needs support from the public sector as well. When it comes to consumer protections, regulators must consider what type of crypto legislation will best protect blockchain gamers without dampening innovation for web3 game projects and developers. And law enforcement must consider whether people should be prosecuted for crimes that their avatars commit in the metaverse. To some today, that possibility may seem distant. Yet, virtual reality gaming environments in the web2 world already contend with how to handle things like sexual harassment in the metaverse. As for positive developments between virtual reality and blockchain gaming, soon enough, blockchains could be used to facilitate ownership and trading of virtual real estate.
Ultimately, for blockchain gaming projects to gain popularity and a greater share of the crypto economy, more basic web3 education is needed so that traditional gamers feel comfortable enough to try crypto gaming. Expanded incentives for crypto gaming novices and veterans alike will grow the user base, too. And, most importantly, the games must be fun. The more players, developers, and investors get involved, the more opportunity blockchain gaming has to contribute significant value to the crypto ecosystem, whether by increased revenue, job creation, or the reputational boost of another positive web3 use case. Because crypto is here to stay, blockchain gaming also presents a unique opportunity for young gamers to get a headstart on learning about crypto now, and the chance to invest in this innovative asset class.
This website contains links to third-party sites that are not under the control of Chainalysis, Inc. or its affiliates (collectively “Chainalysis”). Access to such information does not imply association with, endorsement of, approval of, or recommendation by Chainalysis of the site or its operators, and Chainalysis is not responsible for the products, services, or other content hosted therein.
This material is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to provide legal, tax, financial, or investment advice. Recipients should consult their own advisors before making these types of decisions. Chainalysis has no responsibility or liability for any decision made or any other acts or omissions in connection with Recipient’s use of this material.
Chainalysis does not guarantee or warrant the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, suitability or validity of the information in this report and will not be responsible for any claim attributable to errors, omissions, or other inaccuracies of any part of such material.
